Rockhounding Reddish Rocks, the art and science of collecting rocks and minerals, captivates enthusiasts of all ages. Whether you’re an experienced collector or just starting out, discovering the beauty and diversity of Rockhounding Reddish Rocks and minerals can be an exhilarating journey. In this article, we’ll explore various types of reddish rocks, their properties, how they form, and where to find them. We’ll also touch on their uses and highlight famous formations around the globe. So grab your tools and let’s dig in!
Understanding Rockhounding
Rockhounding refers to the hobby of searching for and collecting rocks, minerals, and fossils. This pursuit not only allows individuals to connect with nature but also provides educational opportunities about Earth’s geology and history. From gemstones to crystals, the variety in rock types can be astonishing.
Historically, rockhounding emerged as a popular pastime in the 19th century. It allowed enthusiasts to appreciate the natural beauty of minerals while also pursuing scientific inquiry. Today, rockhounding is more than just a hobby; it’s a way to explore the earth’s geology, ecology, and even history.
Reddish Rocks and Minerals: An Overview

Reddish rocks and minerals derive their color primarily from iron and other metal oxides. These red minerals often stand out in collections due to their striking hues. The formation processes of these rocks vary, encompassing metamorphism, hydrothermal alteration, and sedimentary processes.
Characteristics of Reddish Rocks
- Color Variations: The intensity of red can range from pale pink to deep crimson, influenced by the mineral composition.
- Formation Processes: Common processes include metamorphism and hydrothermal alteration, where temperature and pressure transform minerals over time.
Geological Significance
Understanding the geological background of reddish rocks can enhance your appreciation of them. Many red rock formations represent significant periods in Earth’s history, providing insight into ancient environments.
Types of Reddish Rocks and Minerals
Let’s dive into some specific reddish rocks and minerals, exploring their properties, formation processes, and where to find them.
Ruby
- Chemical Formula: Al₂O₃(Cr³⁺)
- Hardness: 9 (Mohs scale)
- Formation: Rubies form through the metamorphism of aluminum and chromium-containing rocks.
- Locations: Rubies are found in places like Myanmar, Thailand, and parts of Africa.
Rubies are not only stunning but also one of the hardest gemstones, making them highly desirable for jewelry. The vibrant red color symbolizes passion and energy, contributing to its popularity.
Cinnabar
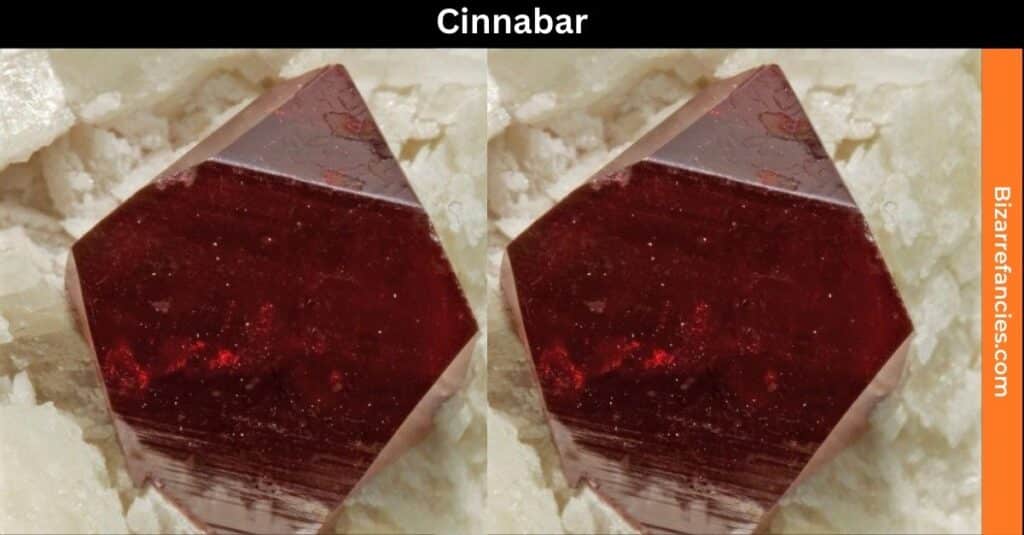

- Chemical Formula: HgS
- Hardness: 2-2.5 (Mohs scale)
- Formation: Cinnabar forms through the hydrothermal alteration of mercury-containing rocks.
- Locations: Notable locations include Spain and the USA, particularly in California.
This mineral is known for its rich red color but is primarily valued for its mercury content, making it a critical mineral in industrial processes.
Garnet
- Chemical Formula: R₃R₂(SiO₄)₃ (common: Almandine)
- Hardness: 6.5-7.5 (Mohs scale)
- Formation: Garnets form through the metamorphism of iron and aluminum-containing rocks.
- Locations: Garnets are commonly found in the USA, India, and Sri Lanka.
Garnets come in various colors, with red being the most recognized. They are often used in both jewelry and as abrasives due to their durability.
Spinel
- Chemical Formula: MgAl₂O₄
- Hardness: 8 (Mohs scale)
- Formation: Spinel forms from the metamorphism of magnesium and aluminum-rich rocks.
- Locations: Notable deposits are found in Myanmar and Sri Lanka.
Spinel is frequently mistaken for ruby and sapphire but is a unique gemstone in its own right. Its vibrant red color and hardness make it a great choice for collectors.
Hematite
- Chemical Formula: Fe₂O₃
- Hardness: 5-6 (Mohs scale)
- Formation: Hematite forms from the oxidation of iron-bearing minerals.
- Locations: This mineral is widely found in locations like the USA, Brazil, and Australia.
Hematite is known for its metallic luster and reddish color. It’s often used in jewelry and as an iron ore.
Rhodocrosite
- Chemical Formula: MnCO₃
- Hardness: 3.5-4 (Mohs scale)
- Formation: Rhodocrosite forms through hydrothermal alteration of manganese-containing rocks.
- Locations: Significant deposits exist in Argentina and the USA.
With its beautiful pink to red hues, rhodocrosite is highly sought after for its aesthetic appeal and is often used in jewelry.
Carnelian
- Chemical Formula: SiO₂
- Hardness: 6.5-7 (Mohs scale)
- Formation: Carnelian forms through hydrothermal alteration of silica-rich rocks.
- Locations: Commonly found in India, Brazil, and the USA.
Carnelian is known for its translucent reddish-orange color. It’s a popular gemstone for beads and carvings, valued for its beauty and durability.
Rubellite
- Complex Chemical Formula: (Boron silicate minerals)
- Hardness: 7-7.5 (Mohs scale)
- Formation: Rubellite forms through the metamorphism of boron-containing rocks.
- Locations: Found in Brazil, Afghanistan, and Nigeria.
Rubellite, a variety of tourmaline, showcases vibrant red to pink hues, making it a coveted gemstone.
Precious Coral
- Chemical Formula: CaCO₃
- Hardness: 3-4 (Mohs scale)
- Formation: Precious coral forms through the growth of coral polyps in marine environments.
- Locations: Found in the Mediterranean Sea and around Japan.
Used in jewelry for centuries, precious coral is valued for its unique colors and textures.
Red Jasper
- Chemical Formula: SiO₂
- Hardness: 6.5-7 (Mohs scale)
- Formation: Red jasper forms through the sedimentary deposition of silica-rich solutions.
- Locations: Commonly found in India, the USA, and Australia.
Properties of Reddish Rocks and Minerals
Understanding the properties of these reddish minerals can enhance your rockhounding experience.
| Mineral | Hardness (Mohs) | Chemical Formula | Specific Gravity | Luster |
| Ruby | 9 | Al₂O₃(Cr³⁺) | 4.0 | Vitreous |
| Cinnabar | 2-2.5 | HgS | 8.1 | Adamantine |
| Garnet | 6.5-7.5 | R₃R₂(SiO₄)₃ | 3.5-4.3 | Vitreous to Resinous |
| Spinel | 8 | MgAl₂O₄ | 3.6-4.1 | Vitreous |
| Hematite | 5-6 | Fe₂O₃ | 5.3-5.5 | Metallic |
| Rhodocrosite | 3.5-4 | MnCO₃ | 3.6-3.9 | Vitreous to Pearly |
| Carnelian | 6.5-7 | SiO₂ | 2.6-2.7 | Vitreous |
| Rubellite | 7-7.5 | Complex boron silicate | 3.0-3.2 | Vitreous |
| Precious Coral | 3-4 | CaCO₃ | 2.6-2.7 | Subvitreous |
| Red Jasper | 6.5-7 | SiO₂ | 2.6-2.7 | Vitreous |
Key Properties Explained
- Hardness: Indicates the mineral’s resistance to scratching. For example, rubies are extremely hard, making them suitable for daily wear in jewelry.
- Specific Gravity: This measures the density of a mineral, which can help identify it in the field.
- Luster: The way light interacts with the surface of a mineral, influencing its aesthetic appeal.
Uses of Reddish Rocks and Minerals
The versatility of Rockhounding Reddish Rocks and minerals extends beyond mere collection. They serve various purposes across different fields.
Jewelry Making

Many reddish minerals, such as rubies, garnets, and carnelian, are popular in jewelry. Their vibrant colors and hardness make them ideal for rings, necklaces, and bracelets.
Pigment Production
Some minerals, particularly hematite, are used in pigment production. Hematite’s rich red color is perfect for art and construction materials.
Mercury Extraction
Cinnabar is the primary source of mercury, crucial in various industrial applications. Understanding its formation and locations can aid in responsible prospecting.
Scientific Research
Geologists study reddish rocks to understand Earth’s history and formation processes. Each mineral tells a story about the conditions under which it formed, providing valuable insights into past environments.
Famous Reddish Rock Formations
Exploring famous reddish rock formations can deepen your appreciation for rockhounding. Here are some notable locations:
- Grand Canyon, Arizona, USA: Known for its stunning red rock layers, the Grand Canyon showcases millions of years of geological history.
- Red Beds, Texas, USA: These formations are famous for their vivid red coloration, resulting from iron oxidation.
- Red Rocks Park, Colorado, USA: A natural amphitheater surrounded by stunning red sandstone formations, perfect for outdoor concerts.
- Monument Valley, Utah, USA: Iconic for its towering red sandstone buttes, often seen in Western films.
- Uluru (Ayers Rock), Australia: A massive sandstone monolith that appears red at sunrise and sunset, deeply significant to Indigenous Australians.
- Sedona, Arizona, USA: Known for its stunning red rock formations, Sedona attracts tourists and rockhounds alike.
- Bryce Canyon National Park, Utah, USA: Features unique rock formations known as hoodoos, showcasing striking Rockhounding Reddish Rocks.
Tips for Successful Rockhounding
Must Read:https://bizarrefancies.com/rockhounding-tennessee-map/
To make the most of your rockhounding adventures, consider these helpful tips:
Tools and Gear
- Rock Hammer: Essential for breaking rocks and extracting specimens.
- Safety Goggles: Protect your eyes when chipping away at rocks.
- Collecting Bags: Use durable bags to store your finds.
Safety Precautions
- Research Locations: Always check regulations and guidelines for rock collecting in specific areas.
- Stay Hydrated: Bring plenty of water, especially in hot environments.
- Wear Appropriate Clothing: Dress for the weather and terrain, including sturdy boots.
Best Practices
- Ethical Collecting: Take only what you need, and leave no trace of your presence.
- Respect Nature: Avoid disturbing wildlife and ecosystems.
Conclusion
Rockhounding offers a unique blend of adventure, education, and appreciation for the natural world. From stunning reddish rocks and minerals to famous formations, the journey into the Earth’s geology is both rewarding and enriching. Whether you’re searching for rubies or carnelian, each specimen tells a story that enhances our understanding of the planet Rockhounding Reddish Rocks

Emmanuel is a passionate rockhound and dedicated to exploring the fascinating world of geology and mineral collecting. With years of experience in the field, he shares his adventures and insights through engaging articles and captivating stories. website, Bizarrefancies.com, serves as a hub for fellow enthusiasts, offering tips, guides, and a glimpse into the beauty of nature’s treasures. Join Emmanuel on his journey to uncover the hidden gems of our planet!